Bootstrap Form Template
Introduction
Bootstrap grants a number of form regulation looks, layout features, and custom elements for creating a variety of Bootstrap Form Elements.
Forms offer the optimal option for gaining several feedback from the visitors of our pages. On the occasion that it is really a simple connection or else registration form including just a only a few areas as well as a complicated and nicely thought inquiry the Bootstrap 4 structure got all things that is actually really needed to accomplish the task and obtain great responsive appeal.
By default located in the Bootstrap framework the form aspects are styled to span the whole size of its parent element-- this stuff gets achieved by committing the
.form-control.form-groupBootstrap Form Elements commands
Bootstrap's form commands develop upon our Rebooted form appearances with classes.
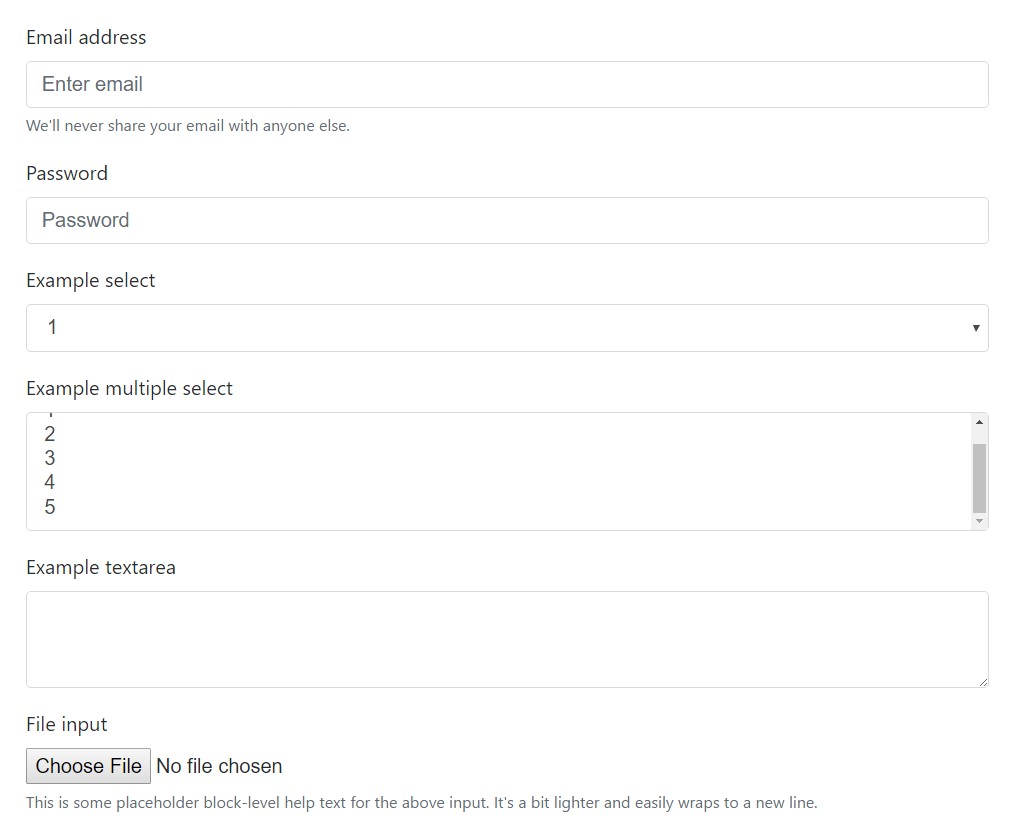
Utilize these classes to opt in to their customized displays to get a more regular rendering around equipments and internet browsers . The example form shown below illustrates common HTML form components that earn updated designs coming from Bootstrap with extra classes.
Always remember, considering that Bootstrap uses the HTML5 doctype, all of inputs must feature a
type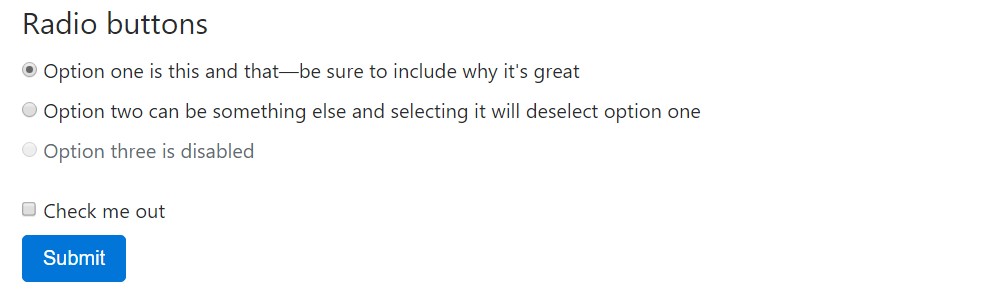
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Email address</label>
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp" placeholder="Enter email">
<small id="emailHelp" class="form-text text-muted">We'll never share your email with anyone else.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect1">Example select</label>
<select class="form-control" id="exampleSelect1">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect2">Example multiple select</label>
<select multiple class="form-control" id="exampleSelect2">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleTextarea">Example textarea</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="exampleTextarea" rows="3"></textarea>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputFile">File input</label>
<input type="file" class="form-control-file" id="exampleInputFile" aria-describedby="fileHelp">
<small id="fileHelp" class="form-text text-muted">This is some placeholder block-level help text for the above input. It's a bit lighter and easily wraps to a new line.</small>
</div>
<fieldset class="form-group">
<legend>Radio buttons</legend>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>
</fieldset>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input">
Check me out
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
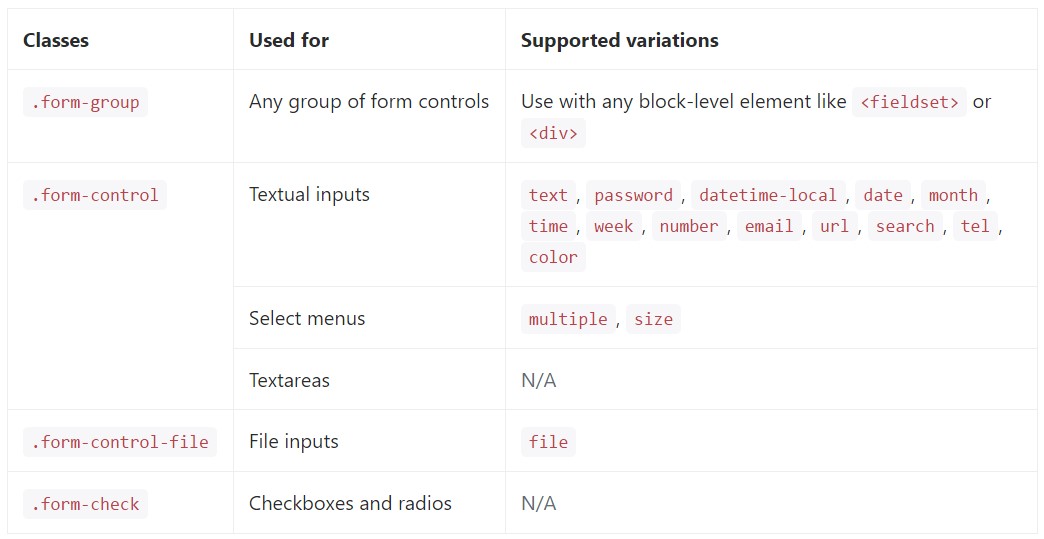
</form>Shown below is a full catalogue of the specific Bootstrap Form Input controls assisted by Bootstrap as well as the classes which personalize them. Supplementary documents is offered for each and every group.
Textual inputs
Listed below are the cases of
.form-control<input>type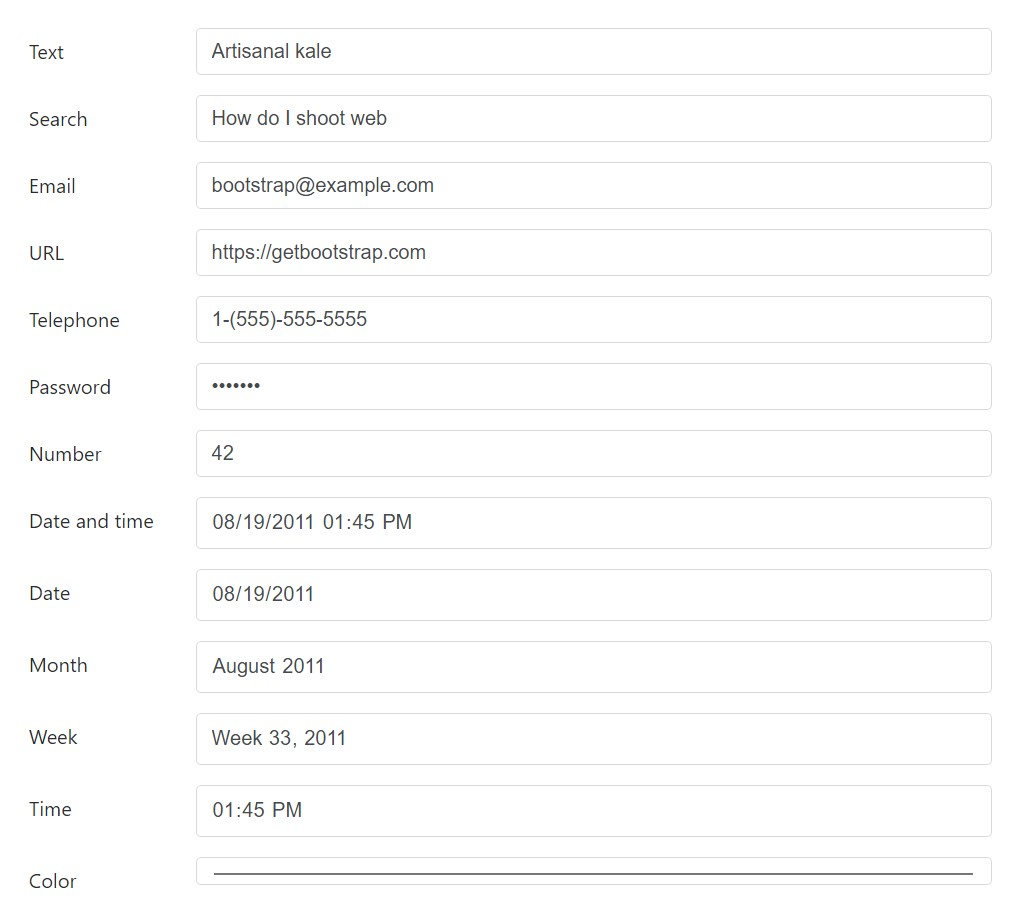
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-text-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Text</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="text" value="Artisanal kale" id="example-text-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-search-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Search</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="search" value="How do I shoot web" id="example-search-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-email-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="email" value="[email protected]" id="example-email-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-url-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">URL</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="url" value="https://getbootstrap.com" id="example-url-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-tel-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Telephone</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="tel" value="1-(555)-555-5555" id="example-tel-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-password-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="password" value="hunter2" id="example-password-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-number-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Number</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="number" value="42" id="example-number-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-datetime-local-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Date and time</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="datetime-local" value="2011-08-19T13:45:00" id="example-datetime-local-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-date-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Date</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="date" value="2011-08-19" id="example-date-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-month-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Month</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="month" value="2011-08" id="example-month-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-week-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Week</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="week" value="2011-W33" id="example-week-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-time-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Time</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="time" value="13:45:00" id="example-time-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-color-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Color</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="color" value="#563d7c" id="example-color-input">
</div>
</div>Form arrangements
Due to the fact that Bootstrap uses
display: blockwidth :100%Form groups
The
.form-groupmargin-bottom<fieldset><div>
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="formGroupExampleInput">Example label</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="formGroupExampleInput" placeholder="Example input">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="formGroupExampleInput2">Another label</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="formGroupExampleInput2" placeholder="Another input">
</div>
</form>Inline forms
Employ the
.form-inline- Controls are
display: flex- Controls and also input groups earn
width: autowidth: 100%- Controls only show up inline within viewports which are at least 576px wide to consider small viewports on mobile devices.
You may possibly need to personally deal with the size and alignment of specific form controls plus spacing utilities ( just as displayed below) And finally, be sure to regularly include a
<label>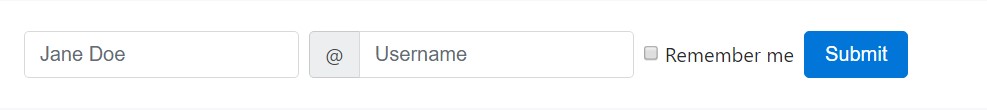
<form class="form-inline">
<label class="sr-only" for="inlineFormInput">Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0" id="inlineFormInput" placeholder="Jane Doe">
<label class="sr-only" for="inlineFormInputGroup">Username</label>
<div class="input-group mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<div class="input-group-addon">@</div>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="inlineFormInputGroup" placeholder="Username">
</div>
<div class="form-check mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox"> Remember me
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>Custom made form controls and picks are likewise assisted.
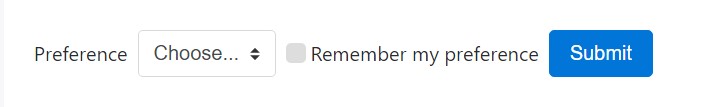
<form class="form-inline">
<label class="mr-sm-2" for="inlineFormCustomSelect">Preference</label>
<select class="custom-select mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0" id="inlineFormCustomSelect">
<option selected>Choose...</option>
<option value="1">One</option>
<option value="2">Two</option>
<option value="3">Three</option>
</select>
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Remember my preference</span>
</label>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>Alternatives to concealed labels
Assistive technological innovations for instance, screen readers are going to have problem using your forms in the case that you don't incorporate a label for each input. For these inline forms, you can certainly conceal the labels utilizing the
.sr-onlyaria-labelaria-labelledbytitleplaceholderplaceholderMaking use of the Grid
For extra structured form layouts which are equally responsive, you can certainly make use of Bootstrap's predefined grid classes or else mixins to set up horizontal forms. Bring in the
.row.col-*-*Be sure to add
.col-form-label<label><legend>.col-form-legend<label>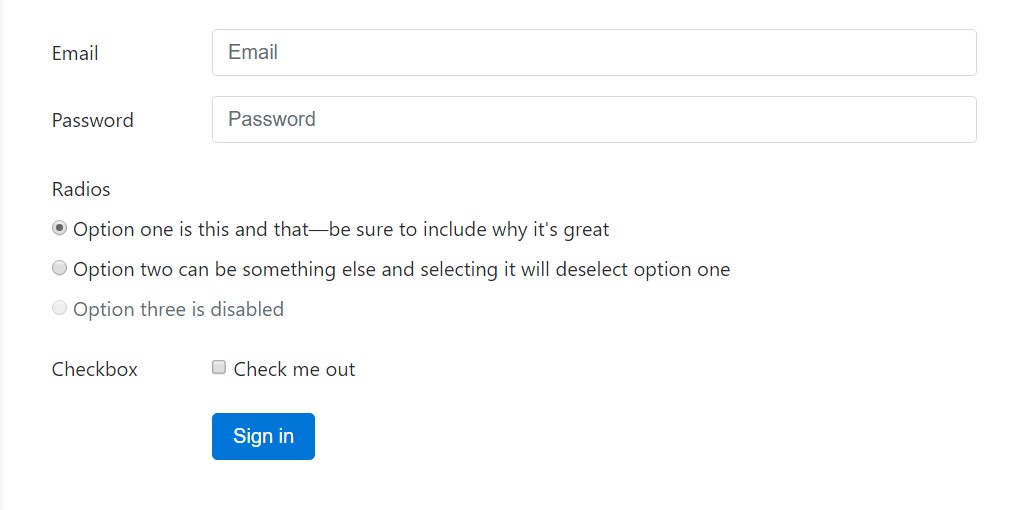
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputEmail3" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="inputEmail3" placeholder="Email">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputPassword3" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword3" placeholder="Password">
</div>
</div>
<fieldset class="form-group row">
<legend class="col-form-legend col-sm-2">Radios</legend>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>
</div>
</fieldset>
<div class="form-group row">
<label class="col-sm-2">Checkbox</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox"> Check me out
</label>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<div class="offset-sm-2 col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Sign in</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
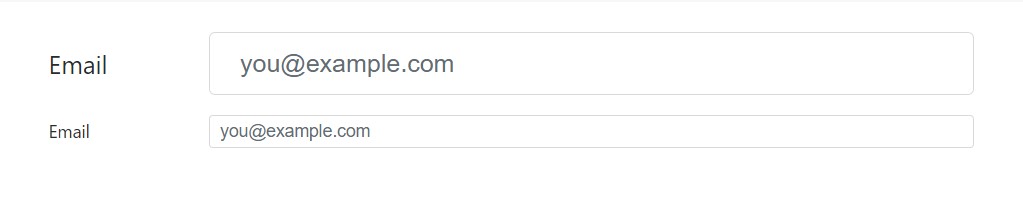
</div>Grid-based form layouts as well sustain large and compact inputs.
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="lgFormGroupInput" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label col-form-label-lg">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-lg" id="lgFormGroupInput" placeholder="[email protected]">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="smFormGroupInput" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label col-form-label-sm">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-sm" id="smFormGroupInput" placeholder="[email protected]">
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Checkboxes and radios
Default radios and checkboxes are raised upon with the support of
.form-checkThe disabled class will at the same time make lighter the text color to help identify the input's state.
Every single checkbox and radio is wrapped in a
<label>- It provides a greater hit areas for checking the control.
- It provides a semantic and practical wrapper in order to help us removed and replace the default
<input>- It produces the state of the
<input>We cover the default
<input>opacity.custom-control-indicator<input>contentWe apply the sibling selector
~<input>: checked.custom-control-description<input>In the checked states, we use base64 embedded SVG icons from Open Iconic. This provides us the best control for styling and positioning across browsers and devices.
Checkboxes

<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>Custom made checkboxes can likewise employ the
: indeterminate
If you are actually applying jQuery, something such as this should be sufficient:
$('.your-checkbox').prop('indeterminate', true)Radios

<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio1" name="radio" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio2" name="radio" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Or toggle this other custom radio</span>
</label>Default (stacked)
By default, any quantity of checkboxes and radios that are immediate relative will be vertically loaded and appropriately spaced by using
.form-check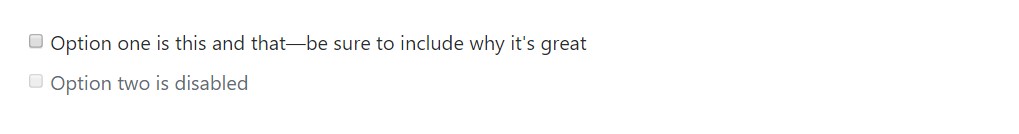
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" value="">
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" value="" disabled>
Option two is disabled
</label>
</div>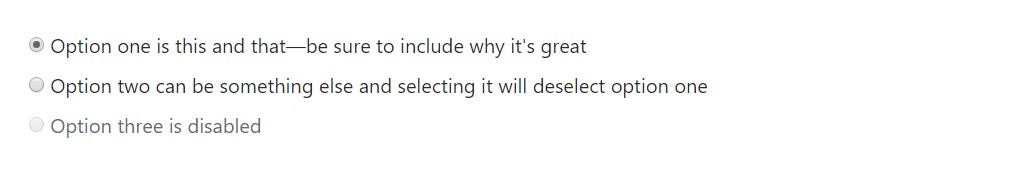
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>Inline
Group checkboxes or else radios on the identical horizontal row through incorporating
.form-check-inline.form-check
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox1" value="option1"> 1
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox2" value="option2"> 2
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox3" value="option3" disabled> 3
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio1" value="option1"> 1
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio2" value="option2"> 2
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio3" value="option3" disabled> 3
</label>
</div>Without having labels
You should not provide a text message in the
<label>aria-label
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="blankCheckbox" value="option1" aria-label="...">
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="blankRadio" id="blankRadio1" value="option1" aria-label="...">
</label>
</div>Static managements
In cases where you need to set plain content near a form label inside a form, use the
.form-control-static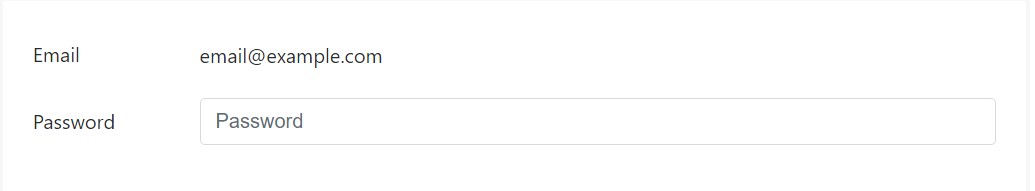
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<p class="form-control-static">[email protected]</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputPassword" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword" placeholder="Password">
</div>
</div>
</form>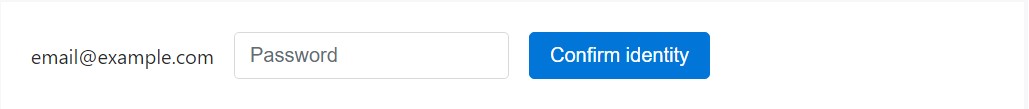
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="form-group">
<label class="sr-only">Email</label>
<p class="form-control-static">[email protected]</p>
</div>
<div class="form-group mx-sm-3">
<label for="inputPassword2" class="sr-only">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword2" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Confirm identity</button>
</form>Disabled states
Put in the
disablednot-allowed<input class="form-control" id="disabledInput" type="text" placeholder="Disabled input here..." disabled>Bring in the
disabled<fieldset>
<form>
<fieldset disabled>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="disabledTextInput">Disabled input</label>
<input type="text" id="disabledTextInput" class="form-control" placeholder="Disabled input">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="disabledSelect">Disabled select menu</label>
<select id="disabledSelect" class="form-control">
<option>Disabled select</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="checkbox">
<label>
<input type="checkbox"> Can't check this
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</fieldset>
</form> Warning relating to hyperlink functions of <a>
<a>By default, browsers will treat all original form controls (
<input><select><button><fieldset disabled><a ... class="btn btn-*">pointer-events: noneCross-browser being compatible
While Bootstrap will apply these particular styles inside all web browsers, Internet Explorer 11 and below don't completely sustain the
disabled<fieldset>Readonly inputs
Add in the
readonly
<input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Readonly input here…" readonly>Control scale
Put heights making use of classes like
.form-control-lg.col-lg-*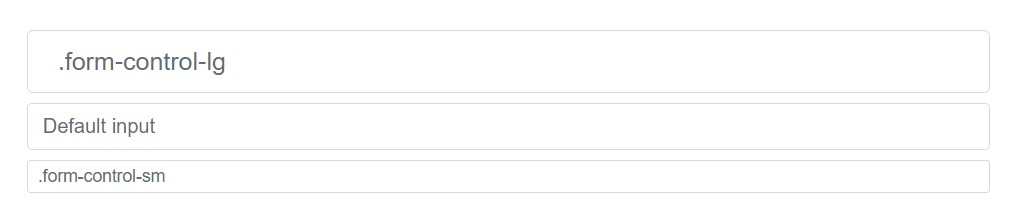
<input class="form-control form-control-lg" type="text" placeholder=".form-control-lg">
<input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Default input">
<input class="form-control form-control-sm" type="text" placeholder=".form-control-sm">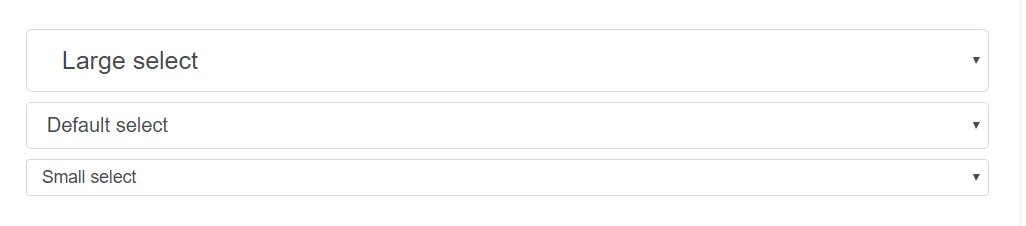
<select class="form-control form-control-lg">
<option>Large select</option>
</select>
<select class="form-control">
<option>Default select</option>
</select>
<select class="form-control form-control-sm">
<option>Small select</option>
</select>Column size
Wrap inputs inside a grid columns, or any kind of customized parent component, in order to quickly enforce the wanted widths.
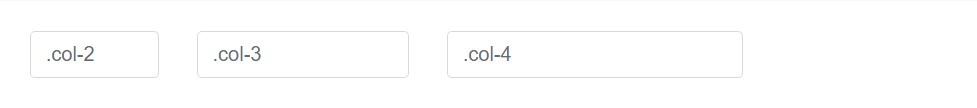
<div class="row">
<div class="col-2">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-2">
</div>
<div class="col-3">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-3">
</div>
<div class="col-4">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-4">
</div>
</div>Assistance text
The
.help-block.form-text.has-feedback.form-control-danger.form-control-warning.form-control-successAssociating help message along with form controls
Assistance text needs to be clearly related to the form control it really relates to utilizing the
aria-describedbyBlock level
Block help message-- for below inputs as well as for longer lines of the assistance content-- can be easily reached with
.form-textdisplay: block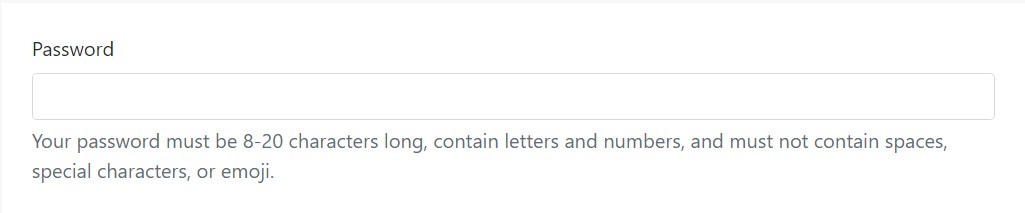
<label for="inputPassword5">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="inputPassword5" class="form-control" aria-describedby="passwordHelpBlock">
<p id="passwordHelpBlock" class="form-text text-muted">
Your password must be 8-20 characters long, contain letters and numbers, and must not contain spaces, special characters, or emoji.
</p>Inline
Inline content have the ability to use any type of common inline HTML feature (be it a 'small', 'span', or another thing).
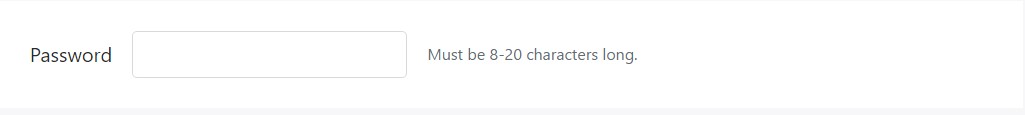
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputPassword4">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="inputPassword4" class="form-control mx-sm-3" aria-describedby="passwordHelpInline">
<small id="passwordHelpInline" class="text-muted">
Must be 8-20 characters long.
</small>
</div>
</form>Validation
Bootstrap features validation formats for success, danger, and warning states on the majority of form controls.
How to utilize
Here's a briefing of exactly how they do the job:
- To use, provide
.has-warning.has-danger.has-success.col-form-label.form-control- Contextual validation message, as well as your standard form field help content, may possibly be included together with the use of
.form-control-feedback.has-*margincolor- Validation icons are
url()background-image- You may operate your own base64 PNGs or perhaps SVGs with upgrading the Sass variables and recompiling.
- Icons are able to additionally be disabled completely by preparing the variables to
noneIdentifying conditions
Usually stating, you'll want to work with a certain state for particular styles of responses:
- Danger is perfect for the moment there's a blocking or required field. A user has to submit this specific field successfully to submit the form.
- Warning performs properly for input values which are in progression, like parole strength, or soft validation just before a user attempts to submit a form.
- And lastly, success is perfect for instances when you have per-field validation through a form and want to stimulate a user through the rest of the fields.
Good examples
Here are some examples of the aforementioned classes in action. First off is your standard left-aligned fields with labels, help content, and validation messaging.

<div class="form-group has-success">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputSuccess1">Input with success</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-success" id="inputSuccess1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Success! You've done it.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-warning">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputWarning1">Input with warning</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-warning" id="inputWarning1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Shucks, check the formatting of that and try again.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-danger">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputDanger1">Input with danger</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-danger" id="inputDanger1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Sorry, that username's taken. Try another?</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>All those same states can easily in addition be applied together with horizontal forms.

<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row has-success">
<label for="inputHorizontalSuccess" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-success" id="inputHorizontalSuccess" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Success! You've done it.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row has-warning">
<label for="inputHorizontalWarning" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-warning" id="inputHorizontalWarning" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Shucks, check the formatting of that and try again.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row has-danger">
<label for="inputHorizontalDnger" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-danger" id="inputHorizontalDnger" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Sorry, that username's taken. Try another?</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Radios and checkboxes are as well sustained.

<div class="form-check has-success">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxSuccess" value="option1">
Checkbox with success
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check has-warning">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxWarning" value="option1">
Checkbox with warning
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check has-danger">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxDanger" value="option1">
Checkbox with danger
</label>
</div>Custom-made forms
To get a lot more customization and cross web browser consistency, make use of Bootstrap fully customized form components to substitute the web browser defaults. They're built on very top of semantic and convenient markup, so they are actually solid substitutes for any type of default form control.
Disabled
Custom-made checkboxes and radios can also be disabled . Put in the
disabled<input>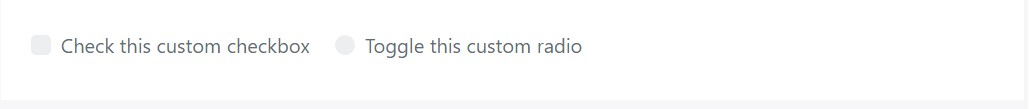
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input" disabled>
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio3" name="radioDisabled" type="radio" class="custom-control-input" disabled>
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>Validation forms
Incorporate the various other states to your customized forms along with Bootstrap validation classes.

<div class="form-group has-success">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-warning">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-danger mb-0">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>Stacked
Custom radios and checkboxes are inline to start. Add in a parent together with class
.custom-controls-stacked
<div class="custom-controls-stacked">
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radioStacked1" name="radio-stacked" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radioStacked2" name="radio-stacked" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Or toggle this other custom radio</span>
</label>
</div>Select menu
Customized
<select>.custom-select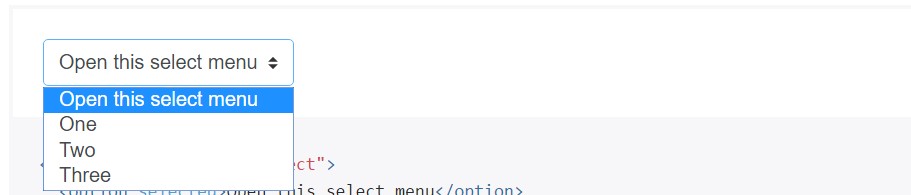
<select class="custom-select">
<option selected>Open this select menu</option>
<option value="1">One</option>
<option value="2">Two</option>
<option value="3">Three</option>
</select>File web browser
The file input is the most gnarly of the bunch and require supplementary JavaScript on the occasion that you want to catch all of them up along with practical Choose file ... and selected file name text.
<label class="custom-file">
<input type="file" id="file" class="custom-file-input">
<span class="custom-file-control"></span>
</label>Here’s The ways to put to use:
- We wrap the
<input><label>- We cover up the default file
<input>opacity- We utilize
: after- We employ
:before- We reveal a
height<input>To puts it simply, it is simply an absolutely customized component, all obtained using CSS.
Turning alternatively customizing the sequences
The
: lang()$ custom-file-textes$custom-file-text: (
placeholder: (
en: "Choose file...",
es: "Seleccionar archivo..."
),
button-label: (
en: "Browse",
es: "Navegar"
)
);You'll need to establish the language of your documentation ( or else subtree thereof) properly in order for the correct message to be revealed. This may be done working with the lang attribute or else the Content-Language HTTP header, among various other solutions.
Conclusions
Fundamentally these are the brand-new features to the form components added within the most recent fourth edition of the Bootstrap system. The entire perception is the classes got extra instinctive and straightforward therefore-- much more simple to apply and using the custom control features we can easily now obtain far more foreseeable appeal of the components we include in the website page we create. Right now all that's left for us is figure out the proper info we would need from our possible site visitors to fill in.
Effective ways to make use of the Bootstrap forms:
Related topics:
Bootstrap forms official documents
Bootstrap article
Support for Bootstrap Forms